Gingival hyperplasia is a condition characterized by the abnormal enlargement of the gums in dogs, leading to various complications, including periodontal disease. This inflammation can create a distressing environment for dogs, often causing discomfort and inviting further complications such as infection. Understanding this condition is crucial for dog owners to recognize early signs and seek timely veterinary intervention.
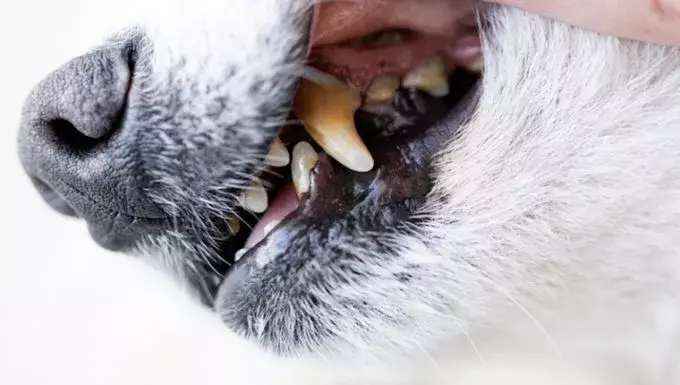
The symptoms of gingival hyperplasia can be alarming for pet owners as they directly affect the dog’s oral health. Common indicators include swollen or thickened gums, the presence of red, inflamed tissue, and noticeable growths along the gum line. Dogs may exhibit behaviors such as chewing or pawing at their mouths, which can exacerbate the problem and lead to self-inflicted injuries. Additional signs include the emergence of pockets in the gums and, in severe cases, bleeding. Recognizing these symptoms promptly can guide owners to necessary veterinary care before the situation escalates.
Several factors can contribute to the onset of gingival hyperplasia. One primary cause is the accumulation of bacteria and plaque along the gum line, which can trigger inflammatory responses. Certain dog breeds are particularly susceptible, including Boxers, Great Danes, Doberman Pinschers, Dalmatians, and Collies—all of which may have a genetic predisposition to develop this condition. Furthermore, there is a notable correlation between the use of immunosuppressant medications and the development of gingival hyperplasia, with these drugs impacting the immune response and potentially leading to gum enlargement.
When it comes to diagnosing gingival hyperplasia, a veterinarian will perform a thorough examination of the dog’s oral cavity. This assessment may be supplemented by diagnostic tools such as X-rays and biopsies to eliminate the possibility of other underlying health issues. Once diagnosed, treatment often involves surgical intervention to remove excess tissue along the gums and repair any structural damage. Pain management is also an essential component during recovery, with veterinarians typically prescribing analgesics to alleviate discomfort.
Additionally, routine deep cleaning of the dog’s teeth will likely be recommended to prevent future occurrences of periodontal disease and maintain overall oral health. Establishing a consistent dental hygiene regimen at home becomes crucial to support your dog’s recovery and long-term wellbeing.
Preventing gingival hyperplasia is largely centered around responsible dental care practices. Regular tooth brushing, professional dental cleanings, and vigilant oral examinations can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease. Pet owners should strive to maintain their dog’s dental health and consult their veterinarian for recommendations tailored to their pet’s specific needs.
By staying informed and vigilant, dog owners can effectively manage and prevent gingival hyperplasia, ensuring their furry companions enjoy better oral health and overall quality of life. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the importance of veterinary care can lead to timely interventions and successful outcomes.

Leave a Reply